Kentucky Public Pensions Authority
The Kentucky Public Pensions Authority (KPPA) is responsible for the investment of funds and administration of pension and health insurance benefits for nearly 444,000 state and local government employees, state police officers, and nonteaching staff of local school boards and regional universities. Daily system activities, including administrative support, investment management, benefits counseling, accounting and payroll functions, and legal services, are performed by a staff of professional employees working as the KPPA.
KPPA covers three separate systems:

CERS and KERS each have members in hazardous and nonhazardous positions, while all SPRS members are considered to be in hazardous positions.
Governance and Administration
The systems are administered by two 9-member boards of trustees, each consisting of three elected members and six gubernatorial appointees serving four-year terms. The governance of CERS rests with the 9-member CERS Board of Trustees. Another 9-member board of trustees called the Kentucky Retirement Systems (KRS) oversees KERS and SPRS. KPPA is governed by a third 8-member board composed of trustees from CERS and KRS.
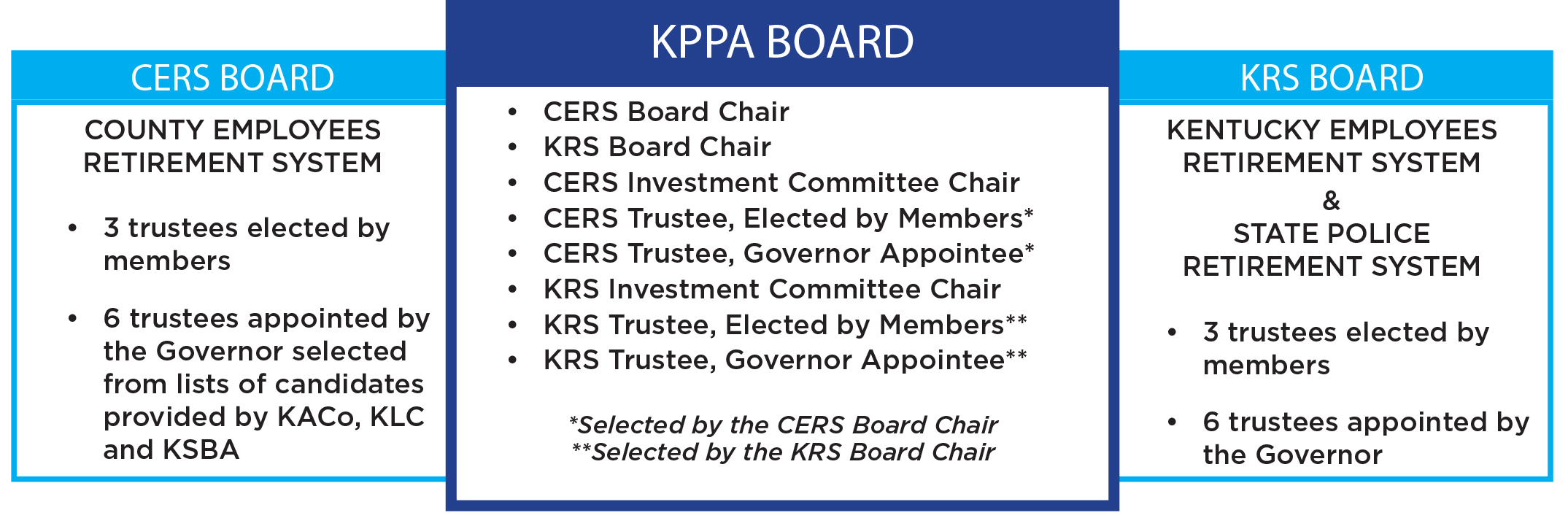
CERS and KRS each have a Chief Executive Officer (CEO), who serves as a legislative and executive advisor to the respective boards, and a General Counsel who provides legal services.
KPPA is led by an Executive Director who works with the CEOs of CERS and KRS to carry out the statutory provisions of the systems.
Economic Impact
In Fiscal Year 2024, KPPA paid over $2 billion in ongoing pension benefits to Kentuckians. These pension payments support state economic activity, with 93% paid to in-state residents. Payments per Kentucky county range from $1.3 million to $375 million annually providing a consistent revenue stream for all local economies. Read more under "Economic Impact" on our
FYI page.
Fully Funded by 2049

The systems’ actuary projects that the pension and insurance funds will be fully funded by 2049 based on:
- The most recent actuarial valuation,
- The closed amortization period set in statute,
- The systems receiving the full Actuarially Determined Employer Contribution each year, and
- All actuarial assumptions are met.
Read more about the financial and actuarial status of CERS, KERS, and SPRS in our Summary Annual Financial Report.
Our Core Values
MEMBER
Enhance member experience through access to information, effective counseling, support, and services.
INVESTMENT
Manage plan assets prudently and effectively to ensure long-term sustainability and continue to seek full actuarial funding by 2049.
TRANSPARENCY
Foster trust and transparency through clear and consistent communication with all stakeholders to support accountability and informed decision-making.
CULTURE
Champion a workforce that supports organizational continuity and high performance through diversity, safety, wellness, professional development, and succession planning.
IMPROVEMENT
Insist on a culture of continuous improvement to ensure excellence remains the standard.
Our History
KERS was created in 1956 by the Kentucky General Assembly to supplement the benefits provided by Social Security. When the first actuarial valuation was completed June 30, 1957, there were 16,000 employees participating in KERS. SPRS and CERS were established in 1958. The first actuarial valuation of SPRS was conducted June 30, 1959. No actuarial valuation of CERS was conducted until June 30, 1960, because the statutes did not authorize retirements from the system prior to July 1, 1960. On June 30, 1960, there were 68 counties and 2,617 employees participating in CERS, and SPRS included 415 state troopers.